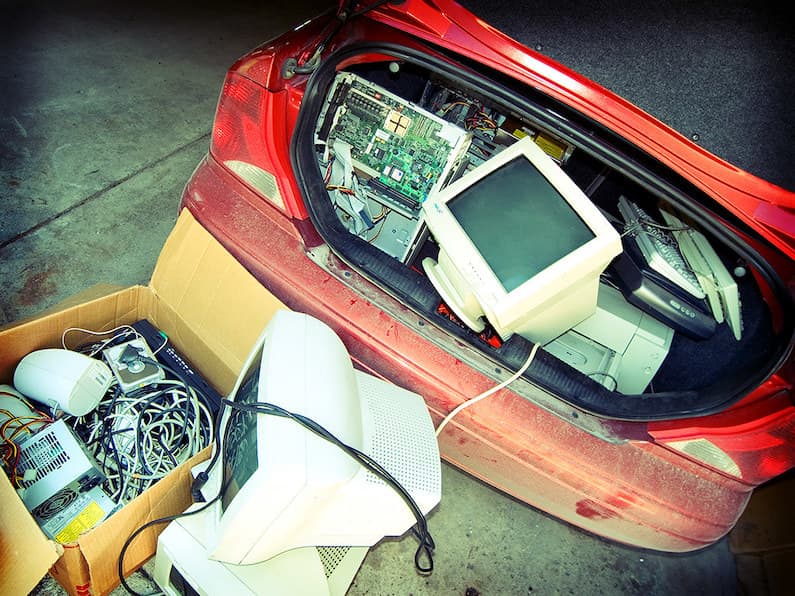
Electronics is one of the world’s largest industries. It’s continually evolving with new technologies emerging every year. Although the continual growth presents exciting opportunities it also leads to a growing problem of electronic waste. Since it’s a relatively new phenomenon there are many myths surrounding electronic recycling. From myths such as you can only recycle old and broken electronics to the myth that recycling makes no environmental difference, these myths are detrimental to the efforts of those attempting to make a difference in the world through electronic recycling. We’ll debunk five of the most common myths about electronic recycling to set the record straight on these myths surrounding electronic recycling.
1. Only Old and Non-Working Electronics Can Be Recycled
Dispelling one of the first myths in our journey, it’s essential to understand that recycling electronics isn’t limited to devices that have ceased to function or are considered outdated. A widespread belief holds that only these categories qualify for recycling, yet this could not be further from the truth. Recycling programs and facilities widely accept electronics in varying states – be they fully operational, slightly used, or completely inoperative. This inclusivity ensures that electronics of all conditions are appropriately handled, preventing unnecessary waste. Encouraging the recycling of functional devices can also play a pivotal role in extending the lifecycle of electronic goods by facilitating their refurbishment and re-entry into the market.
Therefore, before relegating any electronic item to the category of ‘unrecyclable’ due to its operational status, consider the broader acceptance criteria of recycling centers that welcome devices across the functional spectrum.
2. Recycling Electronics Is a Complicated Process
Many people shy away from recycling their electronics, thinking it’s a labyrinthine task filled with complex steps. This belief, however, stands on shaky ground. The truth is, that electronics recycling programs are designed with user convenience in mind. Local recycling centers, electronic retailers, and special e-waste events offer straightforward drop-off procedures, removing any intimidation from the recycling process. Some programs even provide pick-up services for larger items, ensuring ease and efficiency.
Additionally, resources and guides are readily available online to help you prepare your devices for recycling, such as how to wipe personal data or identify recyclable components. This accessibility demystifies the recycling process, highlighting that contributing to environmental sustainability through electronics recycling is not only simple but also actionable for everyone.
3. Deleted Data Can Be Easily Recovered from Recycled Electronics
A common fear deterring individuals from recycling their electronics is the anxiety that personal data, once deleted, can still be retrieved by unscrupulous parties. This concern, while understandable, does not hold up under closer scrutiny. Certified electronics recycling centers adhere to stringent data destruction protocols to ensure complete data erasure from devices before they undergo the recycling process. These procedures are compliant with national security standards, offering peace of mind to consumers worried about data privacy.
Advanced techniques such as data wiping, physical destruction of data storage components, and degaussing are employed to obliterate any remnants of personal information. Thus, the notion that deleted data can be easily recovered from recycled electronics does not reflect the sophisticated data handling practices of professional recyclers committed to safeguarding personal information.
4. Recycling Electronics Does Not Really Make an Environmental Difference
The belief that recycling electronics lacks environmental benefits is a myth that undermines the true value of e-waste management. In reality, responsible electronics recycling plays a crucial role in environmental conservation. It significantly reduces the demand for new raw materials, lowering the environmental strain caused by mining and extraction processes. Furthermore, electronic devices contain hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which, if disposed of improperly, can contaminate soil and water, posing severe risks to wildlife and human health. By ensuring these materials are safely recovered and recycled, we prevent harmful pollutants from entering our ecosystems.
Recycling also conserves energy compared to producing new items from scratch, further amplifying its environmental significance. Each step taken towards recycling electronics is a step away from unsustainable waste management practices, highlighting the indispensable role recycling plays in preserving natural resources and promoting a healthier planet.
5. All Recycled Electronics End Up Being Shipped Overseas
The myth that all recycled electronics are destined for overseas processing is a significant misunderstanding that skews the perception of recycling practices. Indeed, while certain portions of electronic waste have historically been shipped abroad for disposal or recycling, this does not represent the entirety of the recycling ecosystem. A growing number of recycling facilities within the United States and other countries are equipped to handle e-waste efficiently and ethically, adhering to stringent environmental and safety standards. These facilities process electronics to recover valuable materials, such as metals and plastics, for reuse in new products, thus minimizing the environmental impact.
In selecting a reputable recycler, individuals can contribute to a recycling chain that prioritizes local processing and supports the circular economy. This approach not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance waste transport but also ensures that the recycling process adheres to the highest environmental and ethical standards.
Electronic Recycling Solutions from Potomac eCycle
Our commitment to the highest standards ensures your devices are handled responsibly, emphasizing data security and environmental preservation. Join us in making a difference by choosing Potomac eCycle for your recycling needs. Together, we can debunk myths and pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future.
The post Busting 5 Common Misconceptions About Electronic Recycling appeared first on Potomac eCycle.